It can be tough to get the information you need about animals. If you’ve ever wanted to know all there is to know about Northern Andean Deer, then this guide is for you.
What is Northern Andean Deer?
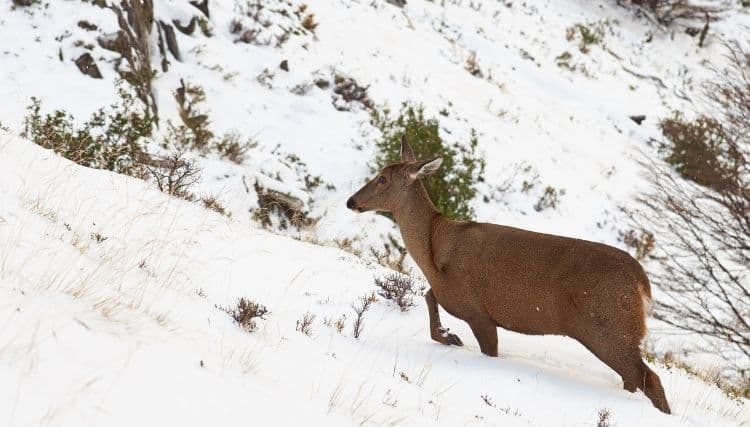
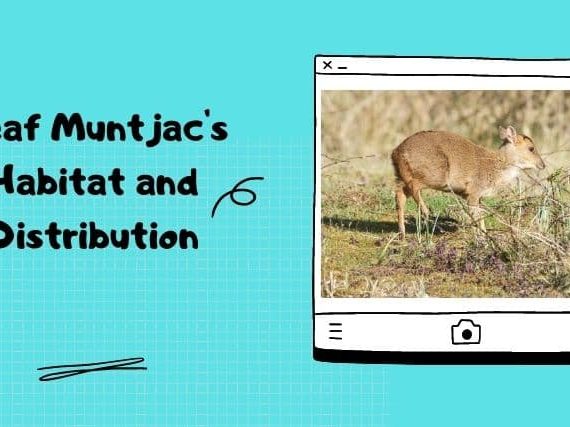
The Northern Andean Deer is native to the northern Andes Mountains. It has brown velvety fur with a white tail and it feeds mostly on leaves, berries, and fruit.
The female deer often give birth to two or three fawns each year which stay close to their mother for about a year before they start exploring on their own.
What is Northern Andean Deer Size?
The size of the northern Andean deer is about 80 cm at the shoulder. It can weigh up to 140 kilograms. It has a body length of about 1 meter.
Where Are Northern Andean Deer Found?

Where Are Northern Andean Deer Found?
The Northern Andean deer are found in the mountains of Colombia, Ecuador, Bolivia, Peru, Venezuela, and Argentina.
These are not endangered animals but they are still on the IUCN Red List of Endangered Species. They are threatened by habitat loss both due to human encroachment on their natural habitat or due to climate change.
Habitat For Northern Andean Deer
The habitat for this species is typically high-altitude grasslands and forests. While they can also be found in the páramo which is a region of alpine tundra higher than 3,000 meters above sea level.
Most sources say they live in mountainous regions but some sources say they live in hills and valleys.
What is The Physical Description Of Northern Andean Deer?
The Northern Andean Deer is a mammal found mostly in the Andes mountains. They are also called Chucura, Huemul, Huemul Deer, South American Red Deer, and Southern Mountain Red Deer. They are usually found at an altitude of 5100 to 6500 feet above sea level.
The males are slightly taller than the females. They have small ears that are rounded at the tips with no hair on them. Their body color is reddish-brown to light brown with lighter legs and heavy body hair.
Older females may have white spots along their back or white stripes on their legs or head while males can have darker patches on their bodies during mating season.
Peruvian Huemul Deer Reproduction -Breeding
The Huemul deer, a northern Andean deer, reproduces during autumn and early winter.
Female Huemul deer reach sexual maturity between the age of three and five years old, while males reach sexual maturity after three to four years.
Breeding season starts as early as November and extends until May.
Males pursue females for mating during the breeding season. The female Huemul deer is pregnant for nine months, with the gestation period beginning in October or November.
How Long Does A Peruvian Huemul Deer Live?
The average lifespan of a Peruvian Huemul deer is 10 years in the wild and 15 years in captivity. The maximum age for a Peruvian Huemul deer in captivity is 25 years.
Peruvian Huemul Deer Communication And Perception
The huemul is a diurnal creature with excellent sight and hearing. The thin membrane of its ears can detect sound up to two miles away, which allows them to hear predators approaching long before they see them.
They are also able to detect seismic vibrations that help them know when it’s safe to go outside or when they should stay inside their burrow.
What Does Peruvian Huemul Deer Eat?
Huemul deer feed on plants from the northern Andes mountains of Peru including grass, roots, and wild celery. They are herbivores and eat grasses and leaves in addition to their diet of lichens.
Peruvian Huemul Deer Anti-predator Adaptations
The Northern Andean deer has a wide range of natural predators that include jaguars, pumas, coyotes, foxes, and birds of prey.
The Huemul deer (Hippocamelus sulcus) is a species of deer that lives in the Andes Mountains in South America. The Huemul has several anti-predator adaptations to protect it from predators.
One adaptation is camouflage, which allows it to blend into its environment and hide from predators. Also, the Huemul has a natural defense mechanism against predators.
If threatened, it will use its antlers to attack predators or they will flee. The Huemuls also have an acute sense of hearing that they use to detect movements from potential predators.
What is Peruvian Huemul Deer Role İn The Ecosystem?
The Huemul deer plays an important role in Peru’s ecosystem through the consumption of vegetation and dispersing seeds throughout the environment. The Huemul deer can also be hunted for their meat which provides income for many Peruvians.
Peruvian Huemul Deer Conservation Status

Peruvian Huemul Deer Conservation Status
Despite their beautiful appearance, Huemul deer are in danger of extinction. The conservation status of the Northern Andean Deer is “Critically Endangered” due to poaching and habitat destruction.
The Peruvian government has recognized the importance of the Huemul and is working to keep them alive. On February 27, 2014, they passed a law that limited hunting for this deer to only two per year and provided funds for protection.
How Many Peruvian Huemul Deers have Left İn The World?
It is difficult to estimate how many Huemul deer remain in Peru because they live in such an isolated region. However, it is estimated that there were about 4,000 in 2006 and now there are less than 2,000 left.
- Facts About Sika Deer Everything You Wanted to Know
- Spotted Deer Chital The Resilient and Vulnerable Habitat Life
- Pere David’s Deer Facts About This Rare Animal Life
- Fascinating Facts About Pampas Deer Life For Hunters
- The Swayne’s Hartebeest Antelope A Wonder Of The African Savannah
How Fast a Peruvian Huemul Deer Run?
They can run at speeds of 40 kilometers per hour and jump over obstacles that are 1.8 meters high.
Do Deer Live İn The Andes Mountains?
The Andean deer is found in Colombia, Ecuador, and Venezuela which is at high elevations between 4500 meters to 6000 meters in the Northern Andes Mountains.
What Kind Of Deer Live İn Patagonia?
Northern Andean Deer can be found in Patagonia, which is a region in Argentina and Chile. The Northern Andean Deer also goes by the name of Pampas Deer due to their location in the Pampas region of South America.
This kind of deer is characterized by having long heads and necks as well as slender bodies with disproportionately short legs to move around on land.
Is The Huemul Extinct?
Huemul, the Northern Andean Deer is on the verge of extinction. The main threat to their survival is hunting and habitat loss.
Why is The Huemul Deer İmportant?
It’s a shame that this deer lives in a place where there is a lot of natural destruction going on. The Huemul deer is an important species because it lives in a special habitat that may be disappearing in the future.
Where Do Northern Andean Deer Sleep?
The Northern Andean Deer often sleep near water sources like rivers and lakes.
What Plants Do Northern Andean Deer Avoid?
The most common plant that they avoid is the ‘Toxicodendron’. This is a plant with leaves that contain a bitter toxic compound called ‘uranin’. The poison can irritate the mouth and throat, as well as stomach pain.
Can Northern Andean Deer Swim?
Northern Andean deer are timid animals that do not like to take risks. They can swim but they will not do it unless they feel threatened.